PITT引领脓毒症护理指导为全国范围内的医院要求进行准备
由于医院为医疗保险和医疗补助服务中心提供的脓毒水果咨询服务中心的医院提供严格任务,该大学匹兹堡医学院审查揭示了基于研究的指导,以改善遵守这种常见和致命的综合征。
败血症是一种危及生命的病情,当身体对感染的反应时出现伤害其自己的组织和器官。它每年超过230,000名美国患者,最初在急诊部门受到最初的护理。尽管有最佳实践,但5人以上的5例化粪池休克患者没有生存。
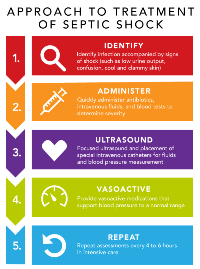
在本周的问题美国医学协会杂志,PITT研究人员将几项高调临床试验的结果纳入了一个简洁的临床诊断和治疗算法,以帮助医院实施国家质量论坛(NQF)严重脓毒症和脓毒休克管理捆绑。
"The NQF sepsis bundle comes on the heels of several high-profile sepsis deaths that highlighted the need for better recognition, prompt treatment and frequent re-assessment of patients with septic shock," said lead author Christopher W. Seymour, M.D., M.Sc., assistant professor in Pitt's departments of Critical Care Medicine and Emergency Medicine. "The sepsis problem is clear, but the solution for patients remains elusive. This new algorithm provides doctors and hospitals with a best-practice approach to assessing and treating septic shock patients as supported by the most recent evidence."
Dr. Seymour and co-author Matthew R. Rosengart, M.D., M.P.H., associate professor in Pitt's Department of Surgery, use their review to stress what is known about good sepsis care - that prompt clinical diagnosis is crucial, and the first step in treatment is promptly addressing the infection. Their review also points out what is less certain, such as various diagnostic and monitoring tools that can be useful in certain subgroups of patients. They highlight new evidence that suggests rigorous, one-size-fits-all septic shock protocols are not superior to good clinical assessments among patients who already received timely treatment. A variety of medications and fluid therapies also can be used to support the patient's circulatory system, but one is not always better than another.
“我们处于一个有趣的时刻,在美国跨越主要政策变革耐心通过败血症,但“正确的”方法仍然有许多不确定性的领域,“Seymour博士说。”作为一开始,我们知道医生必须能够快速诊断败血症并开始毫不拖延地进行治疗。并且他们必须在不同的治疗中得到众所能的,并且哪些可能在不同的地方工作腐败情况。“
进一步探索










用户评论