Dopamine receptor blockade seen as cause for antipsychotic drug side-effects

Since their development in the 1950s, antipsychotic drugs have been widely used to treat psychoses and neuropsychiatric disorders like schizophrenia. A debilitating side-effect of these drugs called parkinsonism limits their efficacy.
University of California, Irvine scientists led by Emiliana Borrelli and colleagues have discovered the key cellular mechanism that underlies the antipsychotic-induced parkinsonism - which includes involuntary movements, tremors and other severe physical conditions. These studies present evidence that will stimulate a targeted approach for the design of novel antipsychotics without side-effects.
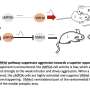
In the journalNeuron, the researchers report that antipsychotics side-effects are due to blockade of the dopamine D2 receptor in a specialized type of neurons in the striatum, called interneurons. Blockade of D2 receptor in these neurons increases neurotransmitter signaling (acetylcholine) above threshold on neighbor neurons leading to motor abnormalities in rodents (catalepsy) and in humans (parkinsonism). Catalepsy is marked by severe muscular rigidity and fixity of posture regardless of external stimuli. Indeed, in mouse studies, the Borrelli team discovered that removing D2 receptors in nerve cells (cholinergic interneurons) did not result in catalepsy in the mice upon antipsychotic treatment.
Borrelli said the importance of this study is twofold. It clarifies a long-waited mechanism that allows to explain the motor side-effects ofantipsychotic drugs并将帮助未来设计的药物剥夺nasty side-effects. It also generates important information for combined therapies (using drugs that block D2 but also acetylcholine receptors) that should be used to improve the life of people treated for debilitating psychiatric disorders.
更多的信息:Neuron,DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.06.014,www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(16)30267-7







.jpg)