Most lungs recover well after COVID-19: study
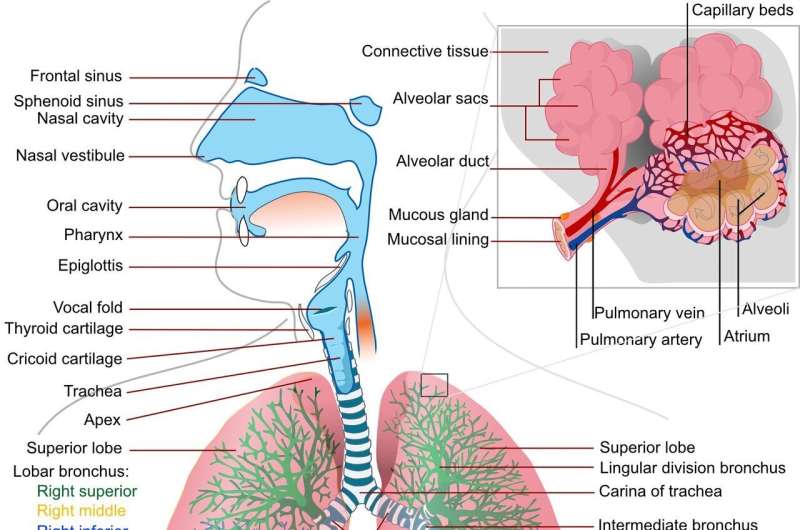
Lung tissue of patients who suffered severely from COVID-19 shows good recovery in most cases. This was revealed by a study carried out by the Radboud university medical center that has now been published inClinical Infectious Diseases. A striking conclusion is that the group who was referred by a GP did not recover as well as patients who were admitted to the hospital's Intensive Care Unit (ICU).
The study, led by pulmonologist Bram van den Borst, included 124 patients who had recovered from acute COVID-19 infections. They visited the Radboud universitymedical centercorona aftercare clinic. The patients were examined by CT scan, alungfunctional test and more. After three months, the researchers took stock, which revealed that the patients' lung tissue is recovering well. Residual damage in the lung tissue was generally limited and is most often seen in patients who were treated in the ICU.
The most common complaints after three months are fatigue, shortness of breath and chest pains. Many people also still experience limitations in their daily life as well as a decreased quality of life. Main researcher and pulmonologist Bram van den Borst explains: "The patterns we see in these patients show similarities with recovery after acute pneumonia oracute respiratory distress syndrome(ARDS), in which fluid accumulates in the lungs. Recovery from these conditions also generally takes a long time. It is encouraging to see that lungs after COVID-19 infections exhibit this level of recovery."
Referred patients do not recover as well as admitted patients
Patients were divided into three categories for the study: a group with patients who were admitted to the ICU, a group of patients who were admitted to a nursing ward in the hospital, and finally a group with patients who could stay home but experienced persisting symptoms that eventually warranted a referral from their GP.
这项研究评估病人如何表现在三months and revealed that the patients who were referred to the aftercare clinic by their GP showed the worst recovery in the following period. Of course, this latter group of patients was referred because of their persisting symptoms. "However, it does seem that there is a clear subgroup of patients who initially experienced mild COVID-19 symptoms and later kept experiencing persistent long-term complaints and limitations," Bram van den Borst elaborates. "What is striking is that we barely found any anomalies in the lungs of these patients. Considering the variety and seriousness of the complaints and the plausible size of this subgroup, there is an urgent need for further research into explanations and treatment options."
Aftercare clinic for patients with persisting symptoms
Radboud university medical center established the corona aftercare clinic at the Dekkerswald location as a reaction to an observed increase in the signals that a substantial number of COVID-19 patients was experiencing long-term complaints, ranging from coughing, fatigue and shortness of breath to anxiety and physical limitations. At the aftercare clinic, an extensive analysis is performed involving multiple disciplines. Based on this analysis, the care requirements of thepatientsand the subsequent steps are determined. Patients who were admitted at Radboud university medical center with COVID-19 will receive an invitation from the corona aftercare clinic. People who went through COVID-19 from home and are still experiencing symptoms can get a referral from their GP to visit the aftercare clinic as well.
Explore further











User comments