你身体上感染COVID-19的可能性是否更低?
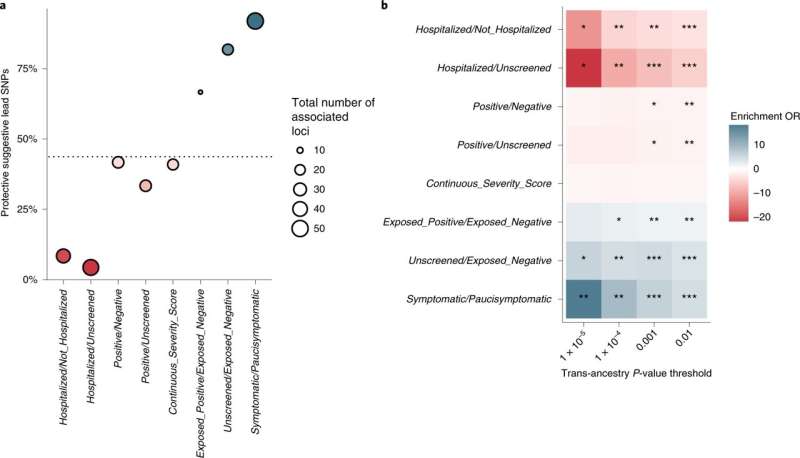 −5) for which the minor allele was protective. The size of each point represents the total number of independent suggestive SNPs for each of the eight phenotypes. The horizontal dashed line represents the mean proportion of protective minor alleles across all eight phenotypes. Point colors match the protective enrichment color scale described in panel b. b, Protective (blue) or risk (red) enrichment at four two-sided CMH enrichment P-value thresholds for each of the eight phenotypes relative to the remaining seven phenotypes. Darker shades correspond to greater magnitude of enrichment (larger CMH OR). Asterisks represent significance of CMH enrichment test (unadjusted two-sided *P < 0.0016; **P < 1 × 10−10; ***P < 1 × 10−100). Credit: Nature Genetics (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41588-022-01042-x" width="800" height="459">
−5) for which the minor allele was protective. The size of each point represents the total number of independent suggestive SNPs for each of the eight phenotypes. The horizontal dashed line represents the mean proportion of protective minor alleles across all eight phenotypes. Point colors match the protective enrichment color scale described in panel b. b, Protective (blue) or risk (red) enrichment at four two-sided CMH enrichment P-value thresholds for each of the eight phenotypes relative to the remaining seven phenotypes. Darker shades correspond to greater magnitude of enrichment (larger CMH OR). Asterisks represent significance of CMH enrichment test (unadjusted two-sided *P < 0.0016; **P < 1 × 10−10; ***P < 1 × 10−100). Credit: Nature Genetics (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41588-022-01042-x" width="800" height="459">
发表在《柳叶刀》上的一项研究提出了三种新定义的表型(个体的可观察到的特征或特征),它们捕获了可能提供对SARS-CoV-2保护的遗传关联自然遗传学.这些发现是通过分析一家DNA检测公司在美国的70多万客户的COVID-19自我报告的结果发现的,这表明这种数据收集方法可以补充COVID-19的临床研究,特别是对较轻病例的研究。
遗传关联研究可以帮助确定基因和生物学途径背后的特定的物理结果或特征。对COVID-19易感性的大规模遗传研究主要集中在与住院有关的严重疾病上。然而,大多数SARS-CoV-2感染不会导致严重疾病,尽管已知许多临床危险因素,如年龄、体重指数或性别,但这些并不能完全解释结果的变化。
克里斯汀·兰德(Kristin Rand)和同事们分析了从一家DNA检测公司的736,723名美国客户(中位年龄57岁;67%的女性)。利用这些基因调查数据,作者分析了四种先前研究的与患糖尿病风险相关的表型严重的疾病.该团队还定义了三种新的保护性表型,这些表型与家庭接触SARS-CoV-2后的感染风险和症状严重程度有关。这些新发现的表型与降低COVID-19风险的遗传密码区域有关,因此可能是治疗干预的有用靶点。
这项研究表明,大规模的、基于调查的直接面向消费者的测试分析可以补充传统的住院人群研究——作者认为这种方法可以应用于未来的其他疾病。
进一步探索