Aversive memory formation in humans involves an amygdala-hippocampus phase code
Memories of aversive or negative events are often remembered more vividly than neutral ones. Although important for survival, resurfacing of past traumatic experiences can trigger psychiatric conditions such as anxiety or post-traumatic stress disorders.
Previous studies indicate that two brain structures, theamygdalaand hippocampus, are essential for this process. The hippocampus is our mainmemoryhub. Damage here, due to Alzheimer's disease for example, leads tomemory loss. The amygdala is important for assessing the emotional content of the environment, particularly for detecting threats. How do the two structures interact to make emotional memories?
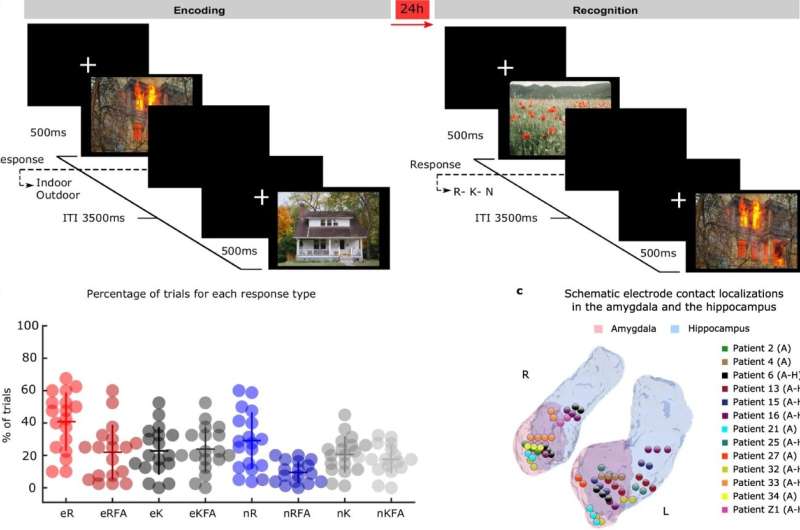
Writing this week inNature Communications, an international group of scientists led by the Laboratory for Clinical Neuroscience in Madrid report the mechanism linking the amygdala and hippocampus during the formation of emotional memories. They studiedelectrical signalsfrom electrodes implanted in the amygdala and hippocampus in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy while these patients performed an emotional memory task.
Patients from the Ruber International Hospital in Madrid and the University Hospital in Zurich were exposed to aversive and neutral scenes. Twenty-four hours later, the visuals were repeated along with novel ones to assess memory recollection. Memory recollection performance was higher for aversive scenes compared to neutral ones. But what happened on the first day, that enabled the emotional memories to be encoded into memory?
The team report that high frequency "gamma" brain activity appeared in the amygdala soon after picture presentation, with the greatest amplitude for emotionally aversive scenes that were remembered a day later. Aversive scenes also triggered transmission of slower "theta" oscillations from the amygdala to the hippocampus.
随后,在hipp伽马活动增加ocampus during emotional and neutral memory formation. The striking observation was that the amount of gamma activity in the hippocampus produced by emotional pictures went up and down with the peak and trough of the amygdala theta oscillation. This is analogous to how amplitude modulated (AM) radio signals are sent. The coupling between amygdala theta and hippocampal gamma was observed in response to all emotionally aversive pictures.
However, what determined whether the aversive picture would be remembered the next day or not, was the point of the amygdala theta oscillation (peak to trough) to which the increased gamma activity was coupled. An identical pattern of organization was found when the team recorded activity from individual brain cells in the hippocampus. This mechanism is a bit like surfing: a surfer needs to be on a particular point of the wave in order to catch it.
The different points of an oscillation—from peak to trough and back to peak—are referred to as its "phase." These findings therefore reveal that aversive memory formation in humans depends on an amygdala-hippocampus "phase code": The amygdala coordinates the neuronal activity in the hippocampus, facilitating the encoding of aversive scenes. Intrigued by why phase of amygdala theta oscillations should be so important, the researchers pushed a bit further.
They discovered that the amygdala theta oscillation works as a timer. The time it took to cycle through the thetaoscillationto the precise phase that permitted successful aversive memory encoding was the time it took for gamma activity bursts in thehippocampusto echo thegammabursts that had occurred in the amygdala.
This mechanism could further shed light on the signaling processes through which the amygdala influences other aspects of cognition, such as perception and decision making, paving the way for targeted therapies against psychiatric disorders.