This article has been reviewed according to Science X'seditorial processandpolicies.Editorshave highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Income rank linked to experience of physical pain, irrespective of whether in a rich or poor country, study suggests
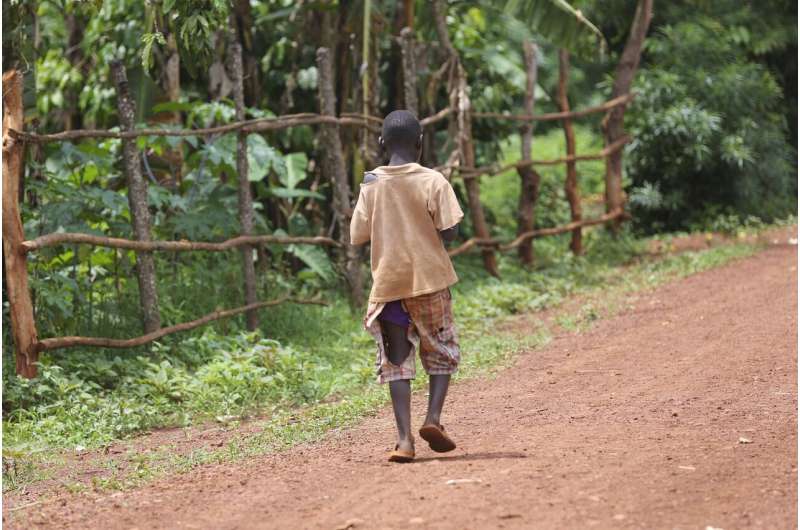

全球民调数据的一项新的研究表明那t a person's income rank relative to their peers is linked to their experience of physical pain, with a lower income rank linked to a higher likelihood of experiencing pain. It is the first time such a relationship has been shown.
The study found the link to persist, to the same degree, irrespective of whether the person lives in a rich country or a poor country.
Income rank is the position of an individual's absolutepersonal incomeamount in a list of those amounts ordered from lowest to highest. The higher the position in the list, the higher theincomerank.
The study, authored by Dr. Lucía Macchia, Lecturer in Psychology at City, University of London, also suggests that people inpoor countries比那些生活在富裕c也好不了多少ountries when it comes to the effect of the absolute amount of personal income they earn on the likelihood of them experiencingpain. This was an unexpected finding and requires further investigation, as the prediction was that those in poorer countries would be more strongly affected, assuming that an increase in absolute income would allow them to obtain more resources to support their well-being that are more readily available in rich countries.
Overall, the study findings suggest that an overriding factor affecting a person's pain levels based on their personal income could benegative emotionsrelated to their appraisal of their income ranking compared to their peers. Whether that be related to their perception of their own levels of deprivation relative to their peers (in keeping with Relative Deprivation Theory) or their standing in a society and a feeling of a lack of social mobility (Social Comparison theory).
In the study, analyses were made of data from the annual World Gallup Poll (GWP), across the years 2009-18, and consisting of responses from approximately 1.3 million adult survey respondents from across 146 countries. Respondents were asked what their total monthly household income was before taxes, which was divided by the number of people in their household to derive the respondent's personal income amount. Respondents were also asked whether they experienced physical pain the day before being surveyed to which they could respond 'yes' or 'no'. In the analyses, linear regression models were created from these data in addition to further ancillary information.
This study refers to pain as the feeling that people experience when their body hurts regardless of the presence of physical damage.
Physical pain is one of the main reasons people visit the accident and emergency room in the UK. Approximately nine million people live withchronic painin the UK and musculoskeletal pain alone accounts for 30 percent of the country's medical consultations.
Physical pain has been increasing dramatically in the last decades, becoming a priority for global public health. Pain affects leisure and productivity at work, increases health care costs, and represents a major challenge for healthcare systems. Pain plays a key role in suicide and in drug and alcohol misuse. In light of these circumstances, understanding the context of pain is crucial to addressing its consequences.
Study author, Dr. Lucía Macchia, said, "This is the first study that shows that income rank and pain are linked around the world. It suggests thatpsychological factorsrelated to the well-known phenomenon of social comparison may influence people'sphysical pain."
The study is published online in the journal,Social Psychological and Personality Science.
更多的信息:Having less than others is physically painful: Income rank and pain around the world,Social Psychological and Personality Science(2023).DOI: 10.1177/19485506231167928